What is Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
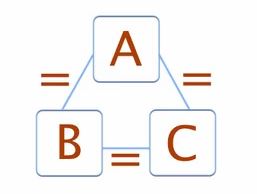
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics is a fundamental principle in the field of thermodynamics that establishes the concept of temperature and thermal equilibrium. This law essentially states that if two bodies, A and B, are separately in thermal equilibrium with a third body, C, then A and B are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. In simpler terms, it asserts that if two systems are at the same temperature as a third system, they are at the same temperature as each other.
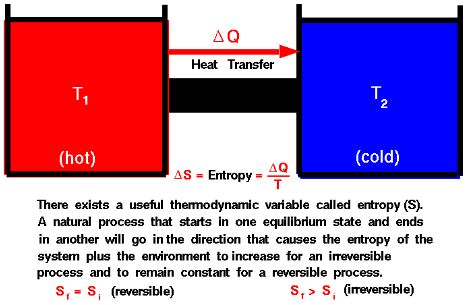
To comprehend this law, it’s crucial to understand the concept of temperature measurement. The temperature of a body is determined by observing changes in a particular physical characteristic, known as a thermometric property. A thermometer, typically consisting of a reference body with a known behavior as a function of temperature, is employed to gauge these changes.
For instance, consider a common mercury thermometer. The mercury is confined in a capillary tube and expands or contracts based on the temperature it is exposed to. When this thermometer is placed in contact with a hot body, like water, the mercury within it absorbs heat and expands until it attains thermal equilibrium with the water. The temperature of the water can then be determined by reading the scale on the thermometer.
This concept can be better illustrated with an example. Suppose we have a vessel filled with hot water. By inserting a mercury thermometer into the water, the mercury inside the thermometer undergoes expansion until it achieves thermal equilibrium with the water. The scale on the thermometer provides a numerical value corresponding to the temperature of the water. The highest point reached by the mercury in the capillary tube signifies the temperature of the water.
In essence, the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics lays the groundwork for temperature measurement and the idea that temperature is a property that can be compared and equated between different systems. It forms a crucial basis for the development of the temperature scales we use today and facilitates our understanding of thermal equilibrium.
Examples that illustrate the application of the Zeroth Law
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics is a fundamental principle that allows us to define and measure temperature. Here are a few examples that illustrate the application of the Zeroth Law:
- Household Thermometers: Everyday thermometers, like those used in homes, rely on the Zeroth Law. When you place a thermometer in your mouth to measure your body temperature, the thermometer is in thermal equilibrium with your body. Similarly, if you place it in a cup of hot coffee, it comes to thermal equilibrium with the coffee. The Zeroth Law ensures that you can compare these temperatures directly because the thermometer is the common reference.
- Cooking Thermometers: Cooking thermometers are often used to measure the temperature of food during preparation. When you insert a cooking thermometer into a piece of meat or a pot of boiling water, the thermometer reaches thermal equilibrium with the substance being measured. This allows you to monitor and control the temperature during cooking.
- Climate and Meteorology: In weather stations and meteorological instruments, the Zeroth Law is applied. Different weather instruments, like mercury or alcohol thermometers, are designed to come to thermal equilibrium with the air to measure ambient temperature accurately. This ensures that temperature measurements across various locations and instruments are consistent.
- Medical Applications: In medical settings, devices such as infrared thermometers, ear thermometers, or temperature probes rely on the Zeroth Law. These instruments come to thermal equilibrium with the body or the specific area being measured, allowing for accurate temperature readings without direct contact.
- Industrial Processes: Various industrial processes require precise temperature control. Instruments and sensors used in these processes, such as those in chemical manufacturing or material processing, adhere to the principles of the Zeroth Law. This ensures that different components or stages of a process are at the same temperature when needed.
- Calibration of Instruments: The Zeroth Law is crucial in the calibration of temperature-measuring devices. Calibration involves comparing the temperature readings of an instrument with those of a reference standard. This reference standard is designed to establish thermal equilibrium easily, ensuring accurate and consistent temperature measurements.
These examples showcase how the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics is applied in diverse areas of our daily lives, industry, and scientific endeavors, providing a foundation for the reliable measurement and comparison of temperatures.
Importance of Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics holds significant importance in the field of thermodynamics and has far-reaching implications in various scientific, industrial, and everyday applications. Here are several reasons highlighting the importance of the Zeroth Law:
- Foundation for Temperature Measurement: The Zeroth Law establishes the concept of thermal equilibrium, allowing for the definition and measurement of temperature. It provides a basis for comparing temperatures between different systems and ensures that temperature is a well-defined and measurable quantity.
- Calibration of Instruments: The Zeroth Law is essential in the calibration of temperature-measuring instruments. Calibration involves establishing a relationship between the response of an instrument and a known temperature. The law ensures that different instruments can be calibrated against a common standard, facilitating accurate and consistent measurements.
- Interpretation of Experimental Data: In scientific experiments involving temperature variations, the Zeroth Law is crucial for interpreting data. It allows researchers to establish thermal equilibrium between different components of an experiment, ensuring that observations and measurements accurately represent the intended physical conditions.
- Design of Thermal Systems: Engineers and designers use the principles of the Zeroth Law when developing thermal systems, such as air conditioning, refrigeration, and heating systems. It ensures that different components within these systems reach thermal equilibrium, leading to efficient and reliable operation.
- Quality Control in Manufacturing: Industries that rely on precise temperature control, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics manufacturing, benefit from the Zeroth Law. It enables the design and operation of processes that require specific temperatures, contributing to quality control and consistent product quality.
- Medical Applications: In the medical field, accurate temperature measurements are vital for diagnostics and patient care. Devices like thermometers, temperature probes, and infrared thermometers adhere to the principles of the Zeroth Law to provide reliable temperature readings in various medical applications.
- Meteorology and Climate Science: Weather stations and climate monitoring instruments employ the Zeroth Law to measure and compare temperatures accurately. This contributes to our understanding of climate patterns, weather forecasting, and the study of environmental changes.
- Energy Efficiency: The Zeroth Law plays a role in optimizing energy efficiency in various systems. Understanding thermal equilibrium is essential for designing energy-efficient processes and systems, minimizing energy waste, and promoting sustainable practices.
- Standardization of Temperature Scales: The Zeroth Law is fundamental to the establishment and standardization of temperature scales, such as Celsius and Fahrenheit. It ensures that temperature measurements are consistent across different instruments and locations.
In summary, the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics is fundamental to our understanding and manipulation of temperature-related phenomena. Its applications extend across scientific research, engineering, manufacturing, healthcare, and environmental studies, contributing to advancements in technology, quality control, and our overall comprehension of the physical world.
Please Subscribe! and Don’t forget to Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, & Linkedin
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
1. What is the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics is a fundamental principle that states if two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. It establishes the concept of temperature and thermal equilibrium.
2. Why is it called the “Zeroth” Law?
It is called the “Zeroth” Law because it was introduced after the First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics, and its importance in defining temperature made it fundamental enough to be considered a foundational law.
3. How does the Zeroth Law relate to temperature measurement?
The Zeroth Law is the basis for temperature measurement. It allows for the definition of temperature and ensures that different measuring instruments can be calibrated against a common standard.
4. What is thermal equilibrium, and why is it crucial in the Zeroth Law?
Thermal equilibrium is a state where two systems have the same temperature. The Zeroth Law relies on thermal equilibrium to establish a common reference point for comparing temperatures between different systems.
5. How is the Zeroth Law applied in everyday temperature measurements, such as with a household thermometer?
Everyday thermometers rely on the Zeroth Law by coming to thermal equilibrium with the substance being measured, such as the human body or a cup of hot coffee, allowing for accurate temperature readings.
6. In what ways does the Zeroth Law impact industrial processes and quality control?
The Zeroth Law is essential in industrial processes, enabling precise temperature control for manufacturing. It contributes to quality control by ensuring consistent and accurate temperature measurements.
7. Can the Zeroth Law be applied in climate science and meteorology?
Yes, the Zeroth Law is crucial in climate science and meteorology. Instruments like thermometers in weather stations adhere to its principles, facilitating accurate measurement and comparison of temperatures.
8. How does the Zeroth Law contribute to energy efficiency in thermal systems?
The Zeroth Law aids in the design of energy-efficient thermal systems by ensuring that different components reach thermal equilibrium, minimizing energy waste and optimizing overall efficiency.
9. What role does the Zeroth Law play in medical applications, such as with infrared thermometers?
In medical applications, devices like infrared thermometers follow the principles of the Zeroth Law, allowing for accurate temperature readings without direct contact with the body, contributing to diagnostics and patient care.
10. How does the Zeroth Law relate to the standardization of temperature scales like Celsius and Fahrenheit?
The Zeroth Law is fundamental to the standardization of temperature scales. It ensures that temperature measurements are consistent across different instruments and locations, leading to the establishment of widely used temperature scales.