The dashboard of your car is equipped with various warning lights that indicate potential issues. Among them, the Check Engine Light is perhaps the most familiar. Typically, this light illuminates as a solid indicator. However, there are different causes (such as bad accelerator pedal sensor, bad EGR valve, bad throttle sensor, or bad engine sensors) of the Check Engine Light starts illumination. It is important to understand what steps to take when faced with a flashing Check Engine Light.
What Does a Flashing Check Engine Light Mean?
When there is a problem with the engine or critical car systems, the Check Engine Light is activated to grab your attention. The Check Engine Light can be triggered by numerous reasons or trouble codes, totaling in hundreds.

However, it is relatively uncommon for the Check Engine Light to flash. If it does flash, it indicates a severe issue that requires immediate attention. The number of potential problems leading to a flashing light is limited, making diagnosis relatively simpler.
Causes of a Flashing or Blinking Check Engine Light
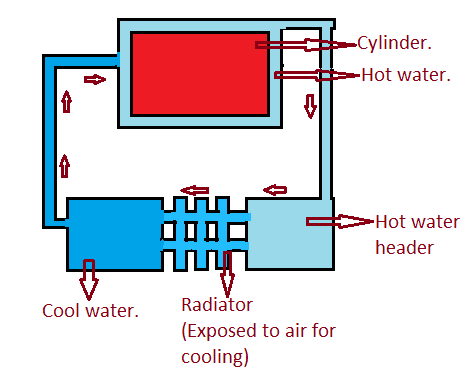
1) Low Coolant Level
One of the primary reasons for a flashing Check Engine Light is a low coolant level, which is a common occurrence. When the coolant level in your car drops below a specific threshold, the light is triggered, serving as a warning for low coolant levels.
2) Bad Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A bad accelerator pedal position sensor (APPS) can cause the check engine light (CEL) to illuminate. The accelerator pedal position sensor is an important component in the electronic throttle control system of modern vehicles. It helps measure the position of the accelerator pedal and communicates this information to the powertrain control module (PCM).
If the APPS malfunctions or sends incorrect signals to the PCM, it can disrupt the proper operation of the throttle system and affect engine performance. The PCM relies on this sensor’s input to determine the appropriate fuel and air mixture for combustion.
3) Bad Catalytic Converter
Your car’s exhaust system includes a catalytic converter, responsible for reducing emissions by converting harmful fumes like carbon monoxide into less damaging by-products.
Additionally, modern vehicles are equipped with oxygen sensors that monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter by analyzing exhaust gas levels. When the oxygen sensor detects inadequate catalyzation, it sends a signal to the vehicle’s powertrain control module (PCM), prompting the activation of the Check Engine Light to alert the driver.
4) Damaged Charging System
It’s important to note that a dead engine may not be solely attributed to a faulty battery; other electrical components such as the alternator or related systems may also be failing to charge correctly. It is crucial to pay attention to this aspect to ensure the proper functioning of the charging system and prevent any potential issues.
5) Engine Misfires
Another cause for a flashing Check Engine Light is an engine misfire, where one or more cylinders fail to generate the expected power. Numerous issues can lead to a misfire, many of which can also result in a flashing Check Engine Light. Examples include fouled spark plugs, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor, or a vacuum leak.
When an engine misfires, you may experience a decline in acceleration and shaking of the car when attempting to accelerate. The vehicle might seem to lose power temporarily, and the engine may exhibit more pronounced vibrations during idle. The challenge with a misfire is that it can occur intermittently or specifically when the engine reaches a certain temperature.
6) Faulty Spark Plugs
When a problem arises with the spark plug in your car, it can trigger the flashing of the check engine light. This situation often occurs when a spark plug becomes coated in oil or overheats, leading to disruptions in engine operation.
However, it’s important to note that the check engine light can also illuminate due to issues with other components like spark plug wires, coil packs, or the catalytic converter.
7) Low Compression
To optimize the engine’s performance, achieving the correct balance of air, fuel, and compression is crucial. Inadequate compression can result in various performance problems.
Some common indicators of compression issues include jerking, power loss, and difficulties with acceleration. Several factors can contribute to compression problems, including damaged piston rings, worn pistons, valve complications, or a defective head gasket. It is important to note that timing belt or chain malfunctions can also impact compression.
8) Overheated Engine
Every vehicle is equipped with a temperature gauge or warning light that indicates the engine’s temperature. When the warning light illuminates, it signifies that the engine’s operating temperature exceeds the normal range.
If the temperature gauge approaches the red zone or reaches its maximum level, it indicates engine overheating. However, it’s worth noting that these indicators may not always function correctly due to a coolant leak, which can cause the sensor to have insufficient coolant to measure accurately.
Frequently asked questions
1.Why is my check engine light flashing, and what does it indicate?
A flashing check engine light typically indicates a severe engine misfire. It suggests that unburned fuel is being dumped into the exhaust system, potentially causing damage to the catalytic converter.
2.Is it safe to drive with a flashing check engine light, or should I pull over immediately?
It’s not advisable to drive with a flashing check engine light. A flashing light signals a serious issue that requires immediate attention. Continuing to drive may cause further damage to the engine or emission control system.
3.What are common causes of a flashing check engine light, and can I diagnose the issue myself?
Common causes include ignition system problems, fuel system issues, or a faulty catalytic converter. While some issues may be diagnosed with basic knowledge, it’s recommended to have a professional diagnostic scan to pinpoint the exact problem.
4.Can a loose gas cap cause the check engine light to flash, or is this more likely related to other issues?
A loose gas cap is a common cause of a steady check engine light, but it’s not typically associated with a flashing light. A flashing light is more indicative of a severe engine problem.
5.How urgent is it to address a flashing check engine light, and what are the potential consequences of ignoring it?
Addressing a flashing check engine light is urgent. Ignoring it can lead to severe engine damage, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. Prompt attention is necessary to prevent further issues.
6.Can weather conditions or temporary factors cause a check engine light to flash, or is it always a sign of a serious problem?
A flashing check engine light is not typically caused by temporary factors or weather conditions. It usually indicates a persistent and serious issue that requires professional attention.
7.How much does it typically cost to repair the issues associated with a flashing check engine light?
The cost of repairs can vary widely depending on the specific issue. Ignoring the problem can lead to more expensive repairs, so addressing it promptly is advisable.
8.Can disconnecting the car battery reset the check engine light, and is this a recommended approach for addressing the issue temporarily?
Disconnecting the battery may reset the light temporarily, but it won’t fix the underlying issue. It’s not recommended as a solution, as the problem will likely recur, and important diagnostic information may be lost.
9.How can I prevent my check engine light from flashing in the future, and are there regular maintenance practices that can help?
Regular vehicle maintenance, including timely oil changes, spark plug replacements, and addressing warning signs promptly, can help prevent issues that may lead to a flashing check engine light.
10.What should I do if my check engine light is flashing intermittently, and the issue seems to come and go?
Even if the flashing light is intermittent, it’s crucial to address it promptly. The issue may still be serious, and waiting to address it could result in more extensive damage to the engine or emission control system.