Dual Cycle:
Dual Cycle is used in fast diesel engines. when diesel is used as fuel in the engine the rpm is high for the dual cycle.
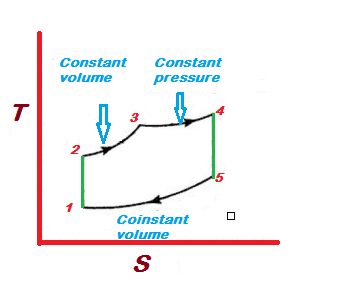
In the Dual cycle, heat addition is partially isochoric and partially isobaric heat addition.
A dual cycle is called a PVS cycle due to the constant pressure process, constant volume process, and isentropic process.
Difference between the Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, and Dual cycle:
The main difference between otto, diesel and dual cycle depends on the thermodynamic process concerned is how you add heat.
In Otto cycle heat addition is Isochoric, i.e Heat is added to the engine when the piston is at the top dead center. which is a constant volume heat addition cycle.
In the Diesel cycle, the heat addition is isobaric i.e Heat is added to the engine at constant pressure process. The diesel cycle is a constant pressure heat addition cycle.
In Dual Cycle heat addition is at isochoric and at isobaric i.e Heat addition to the engine is at constant pressure and at constant volume.
Dual cycle is a conatant pressure and constant volume heat addition cycle.
In the Dual cycle, heat addition is partially isochoric and partially isobaric heat addition.
A dual cycle is called a PVS cycle due to the constant pressure process, constant volume process, and isentropic process.
Diesel cycle is also called a PVS cycle and the Otto cycle is called as VS cycle because of the isentropic and isotropic process.
For same compression ratio:
Otto Cycle > Dual > Diesel
Otto cycle efficiency is more than the dual and diesel cycle.
Dual cycle efficiency is more than the diesel cycle.
Diesel cycle efficiency is less than Otto and dual cycle.
For different compression ratio:
The diesel cycle is more efficient than dual and otto cycle.
Diesel Cycle > Dual > Otto
The efficiency of the S.I (petrol engine) less than C.I (Diesel engine)