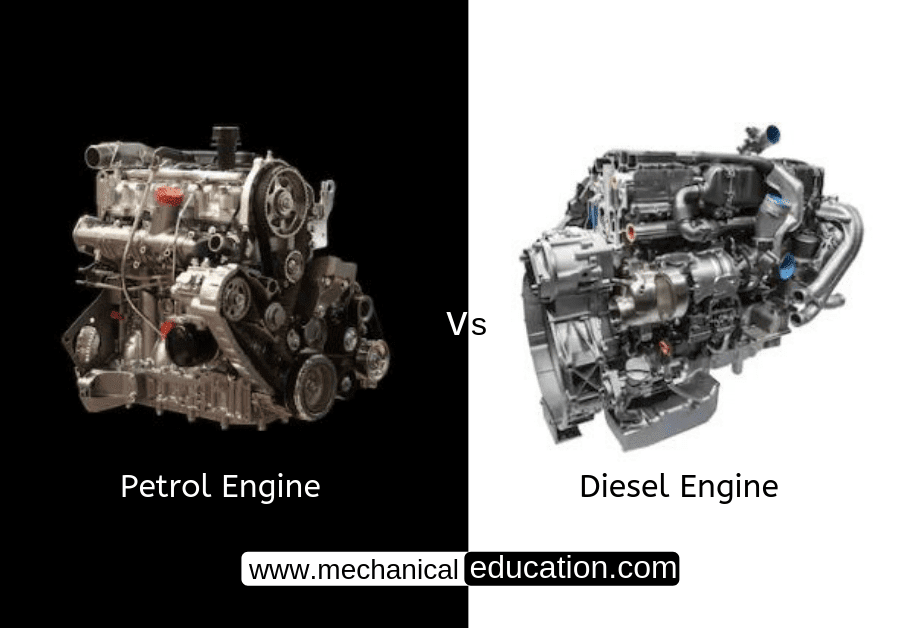
Both gaskets and O-rings are used to create a seal between two surfaces, but they have some key differences in terms of design, function, and application.
Gaskets are typically flat or slightly raised pieces of material that are placed between two surfaces to prevent the leakage of fluids or gases. They can be made from a variety of materials such as rubber, cork, graphite, and PTFE, and are used in a wide range of applications and industries, such as oil and gas, water and sewage treatment, power generation, and chemical processing. Gaskets come in different shapes and sizes, depending on the application and the type of flanges they are used with, like full-face gaskets, sheet gaskets, spiral-wound gaskets and more.
O-rings, on the other hand, are a type of mechanical seal that is made in the shape of a ring with a circular cross-section. They are typically made from rubber, but can also be made from other materials like Teflon, silicone, and nitrile. O-rings are typically used in applications where a smaller, more compact seal is needed, such as in pneumatic and hydraulic systems, engines, and machinery. They are used to seal the connection between two parts that rotate or move in relation to each other. O-ring have specific size, material and pressure rating specifications.
In summary, gaskets are generally used to seal the connection between two flat surfaces, while O-rings are used to seal the connection between two moving or rotating parts. Gaskets are usually larger in size and covers the entire flange face, O-ring are smaller and have a circular cross-section.