Introduction: Whether you drive a diesel engine or a petrol engine, it is important to understand all the components and parts that make up your vehicle’s engine. This knowledge can help you identify any malfunctions that may occur and assist you with troubleshooting and maintenance. Let’s take a look at some of the most common components and parts that make up your engine.
Below are the Engine components and parts
Accessory belt
Air duct
Air intake housing
Air intake manifold
Camshaft
Camshaft bearing
Camshaft fastener
Camshaft follower
Camshaft locking plate
Camshaft pushrod
Camshaft spacer ring
Camshaft phase variator
Connecting rod
Connecting rod bearing
Connecting rod bolt
Connecting rod washer
Crank case & Crank pulley
Crankshaft oil seal (or rear main seal)
Cylinder head
Cylinder head cover
Other cylinder head cover parts
Cylinder head gasket
Distributor
Distributor cap
Drive belt
Engine block
Engine cradle
Engine shake damper and vibration absorber
Engine valve
Fan belt
Gudgeon pin (wrist pin)
Harmonic balancer
Piston
Piston pin and crank pin
Piston ring and circlip
Poppet valve
Positive crankcase ventilation valve (PCV valve)
Pulley part
Rocker arm
Rocker cover
Starter motor
Starter pinion
Starter ring
Turbocharger and supercharger
Tappet
Timing belt
Timing tape
Valve cover
Valve housing
Valve spring
Valve stem seal
Water pump pulley
Accessory Belt
The accessory belt, also known as the drive belt, is responsible for powering many of the accessories in your car such as the air conditioner, power steering pump, alternator and water pump. The accessory belt is connected to several pulleys which spin when your engine is running. If your accessory belt fails, then so will these accessories. It’s important to replace them regularly as they are prone to wear and tear over time.
Air Ducts
Air ducts are responsible for bringing air into your engine from outside sources like an air intake housing or an air intake manifold. Air ducts are usually made from aluminum or plastic and come in various sizes depending on the size of your engine. They also play a role in controlling heat levels within the engine by providing insulation and preventing overheating.
Air Intake Housing
The air intake housing directs cold air into the intake manifold where it can be mixed with fuel to create combustion within the cylinders of your engine. The air intake housing helps regulate temperature levels inside the cylinders while also allowing more oxygen into them which increases combustion efficiency and power output. Without an efficient air intake system, your car won’t perform as well as it should be able too.
Air Intake Manifold
The air intake manifold is connected to both the carburetor or fuel injection system of your car (depending on whether it has a petrol or diesel engine) and its cylinder head(s). When fuel enters through one side of the manifold, cold air is drawn in from outside sources like an air intake housing on another side – this mixture creates combustion within each cylinder when ignited by spark plugs or other ignition systems.
Camshaft
A camshaft is an essential component of any internal combustion engine. It is a shaft that rotates in order to open and close the engine’s valves, controlling the air and fuel mixture that enters the cylinders. There are many different types of camshafts available, including those made from iron, aluminum, bronze, and steel. To ensure your engine operates efficiently and properly, there are several components that need to be in place with your camshaft. In this blog post we will discuss some of these components as well as their importance in keeping your engine running smoothly.
Camshaft Bearings
Camshaft bearings are used to reduce friction between the camshaft and cylinder head as it rotates around its axis. The bearings must be able to withstand high temperatures generated by the constant rotation of the camshaft as well as resist wear caused by contact with other components such as pistons or valves. It is important to regularly check your camshaft bearing for signs of wear or damage so that they can be replaced if needed.
Camshaft Fastener
The camshaft fastener is responsible for holding the camshaft in place within the engine block. It ensures that all of the parts stay connected securely while also providing enough flexibility for proper operation. Different types of fasteners are used depending on the type of vehicle and engine being used, but typically they consist of bolts, studs, screws or pins made from strong metals such as steel or aluminum alloy.
Camshaft Follower
The camshaft follower is a small disc-shaped device mounted on top of a cylinder head that follows the movement of the cams during operation. It helps transfer forces from the cams onto other components such as pistons or valves without causing excessive friction due to its low-friction material composition (typically nylon). The follower also helps reduce noise generated by contact between moving parts within the engine block which can significantly improve performance and efficiency over time.
Camshaft Locking Plate
The locking plate is used to secure all components together when installing a new camshaft into an engine block. It helps keep everything in place until it has been tightened down so that nothing moves out of position during operation which can cause significant damage if left unchecked. The locking plate should always be checked before installing a new camshaft into an engine block since even slight misalignments can lead to dangerous levels of wear and tear over time if not addressed immediately upon installation.
Camshaft Pushrod
The pushrod is responsible for transferring motion from one part of an engine block (e.g., valvetrain) to another (e.g., crankshaft). This part consists primarily of a metal rod with a threaded end which connects two separate connections together during operation allowing them to move relatively freely without binding up due to excessive friction generated during use (as would happen with solid rods). Pushrods should be checked periodically for signs of wear or damage so that they can be replaced when necessary before any major issues arise from their failure within an engine block’s system design.
Camshaft Spacer Ring
The camshaft spacer ring is typically installed between the crankshaft and the camshaft of an engine and serves as a buffer between them. This ensures that there is enough space for both components to move without any interference. The spacer ring also helps reduce vibration because it absorbs part of the shock generated by the engine’s combustion cycle. In addition, it helps dampen noise from the same process, making it quieter and smoother-running in certain types of engines.
Camshaft Phase Variator
The camshaft phase variator is a device used in some engines to improve performance by controlling valve timing throughout operation. This device works by adjusting the position of the valves relative to each other and changing their opening and closing times according to certain parameters such as speed or load. By doing this, it can optimize fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve torque output when needed.
Connecting Rod
The connecting rod is a metal bar that connects the piston to the crankshaft in an internal combustion engine. It is responsible for transferring power from the piston to the crankshaft when it moves up and down during each cycle of operation. The connecting rod must be strong enough to withstand high levels of pressure and heat while still being light enough not to cause too much friction or drag on other components in the engine.
Connecting Rod Bearings
Connecting rod bearings are used to reduce friction between the moving parts of the engine. They act as cushions between the connecting rods and other components such as pistons or crankshafts. This allows them to move freely without causing too much wear and tear on other parts of the engine. The bearings used vary depending on which type of bearing system is installed in the car – either oil-filled or dry-type bearings are typically used.
Connecting Rod Bolts
The bolts hold all of these components together by fastening them into place with nuts or lock washers. Bolts are essential for ensuring that all components remain secure even when subjected to extreme temperatures or vibration from operation. Connecting rod bolts should be inspected regularly for signs of wear and tear as they can become loose over time due to fatigue or improper installation techniques.
Connecting Rod Washer
The washer helps distribute load evenly across all components by providing additional support between them when they are assembled together in an engine block. Washers help prevent damage caused by vibration, misalignment, corrosion, and other environmental factors that can degrade performance over time if left unchecked.
Crank Case & Crank Pulley
Crank cases provide protection for all internal components in an engine block such as pistons, valves, flywheel assemblies, camshafts etc., while crank pulleys provide power transmission between two shafts within an engine block – typically from crankshaft drive gears to main drive gears inside a car’s transmission system – allowing them to rotate properly at variable speeds without stressing out any other part inside it too much while also providing stability during operation under harsh conditions like racing or off-road driving scenarios where shock loads may be present due to uneven terrain or sudden acceleration/deceleration forces exerted onto it from outside sources such as another vehicle passing by etc…
Crankshaft Oil Seal (or Rear Main Seal)
The crankshaft oil seal (or rear main seal) is a rubber ring located in the lower part of the engine block that helps prevent oil from leaking out of the crankcase. The seal should be checked regularly for signs of wear or damage. If it becomes cracked or worn out, it should be replaced immediately. A damaged or worn-out crankshaft oil seal can cause a loss of power or cause your vehicle to overheat due to oil leakage.
Cylinder Head
The cylinder head is one of the most important parts of an engine as it controls combustion by regulating air flow into and out of the cylinders. It should be regularly inspected for signs of wear or damage, such as cracks or warping. If any damage is detected, it should be repaired immediately by a qualified mechanic as failure to do so could result in major engine failure.
Cylinder Head Cover
The cylinder head cover consists of several small metal plates that help protect the valvetrain components from dirt and debris buildup inside the engine block. These plates should be cleaned regularly using an appropriate cleaning solution in order to ensure they remain free from dirt and grime build-up which can lead to decreased efficiency or even engine failure if left unchecked. If any damage is detected on them they should also be replaced immediately with a new set from a reputable source.
Other Cylinder Head Cover Parts
In addition to these metal plates there are also various other parts related to cylinder head covers such as gaskets, o-rings, nuts & bolts etc., which all need regular inspection for signs of wear or damage too. Any damaged parts should be replaced with new ones from a reliable source as soon as possible in order to avoid further damage being caused by dirt and debris build up inside your engine block resulting in reduced efficiency and performance levels.
Cylinder Head Gasket
The cylinder head gasket seals off the top part of the engine where the cylinders meet with each other so that no fuel mixture can escape during combustion cycles leading to improved performance levels overall as well as preventing any potential issues from occurring due to fuel leakage into other areas within your vehicle’s system resulting in costly repairs down the line if not properly maintained on time! Regular inspections are highly recommended here too since any damage found on this component can lead to serious problems like reduced combustion efficiency causing loss in power output or even complete breakdowns if left unchecked long enough!
Distributor
The distributor is an ignition system responsible for distributing high-voltage sparks to the spark plugs in order to ignite the air/fuel mixture inside the combustion chamber. It affects performance by delivering these sparks at optimal times so that your engine runs smoothly.
Distributor Cap – The distributor cap sits on top of the distributor and houses several terminals that connect to each spark plug wire. Its purpose is to protect the terminals from moisture and other debris while also providing a connection point for each spark plug wire. A faulty or worn-down distributor cap can lead to engine misfires or poor performance.
Drive Belt
The drive belt is responsible for powering several accessories within your car such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, A/C compressor and fan. It essentially transfers power from your crankshaft pulley to all of these components in order to keep them running properly. If your drive belt isn’t functioning properly due to wear or damage, you may experience a lack of power when driving or even complete engine failure if essential components are not powered correctly.
Engine Block
The engine block contains all of the vital components needed for your engine to run correctly such as pistons, connecting rods and camshafts. It serves as both a structural support and cooling system for your car’s internal combustion engine. Without it, there would be no way for fuel or air intake needed for combustion nor would there be any way to cool down an overheated engine during operation.
Engine Cradle
An engine cradle provides additional support for your car’s engine block by evenly distributing its weight throughout its frame instead of having it rest on just one spot on the frame itself. This prevents any uneven stress points from occurring which could lead to premature wear or even total failure of the entire structure if left unchecked over time.
Engine Shake Damper & Vibration Absorber
An engine shake damper (also referred to as a vibration absorber) helps reduce vibrations caused by operating an internal combustion engine which can cause discomfort in passengers but also damage certain components over time if not dealt with properly. It works by dampening any vibrations sent through metal parts such as valves or crank shafts before they reach other parts of your vehicle like the chassis and body panels where they can cause even more problems like rattling sounds inside the cabin when driving at highway speeds or above.
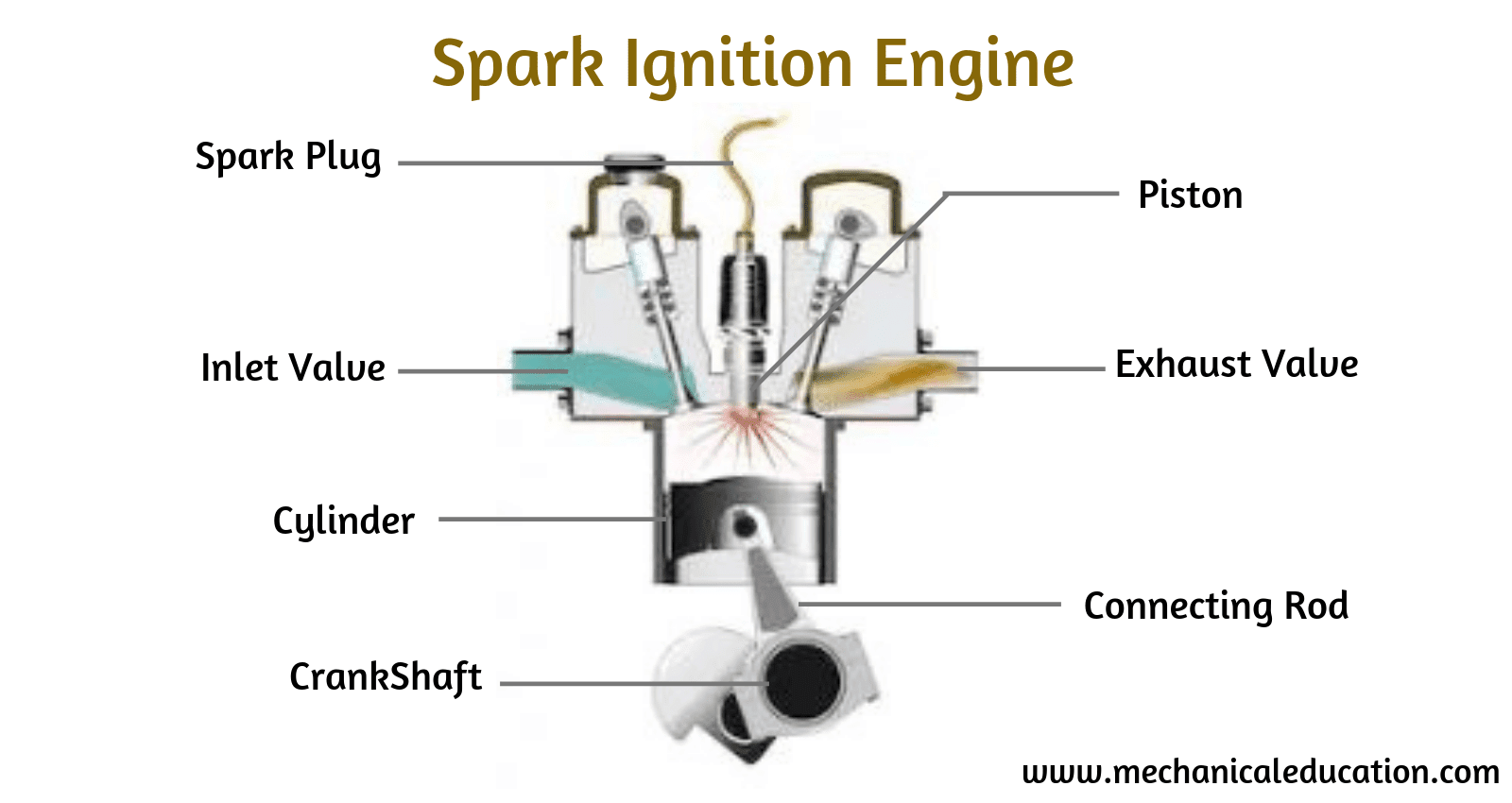
Engine Valve
Your car’s internal combustion process requires air intake which is done via an intake valve located near each cylinder head; exhaust gases are then released through an exhaust valve located near each cylinder head as well. All together these valves help regulate how much fuel enters into each cylinder while also controlling how much exhaust leaves after combustion has occurred; this helps maintain optimal levels of efficiency when operating at peak performance levels throughout extended periods of time without any major issues arising from either end (intake/exhaust).
Fan Belt (also known as serpentine belt):
The fan belt is a long rubber band that runs from the crankshaft to the fan pulley, helping to keep the fan running smoothly. This part is responsible for transferring power from the crankshaft to other components in the engine, such as air conditioning compressors and alternators.
Gudgeon Pin (Wrist Pin):
The gudgeon pin (or wrist pin) is a metal rod that connects a piston to its connecting rod. This part plays an important role in allowing the piston and connecting rod to move up and down without losing contact with each other.
Harmonic Balancer:
The harmonic balancer is responsible for reducing vibrations produced by certain engine components like pistons, rods, and crankshafts. It works by dampening vibrations through its rubber inner core and metal outer shell.
Piston:
A piston is basically a cylindrical component that moves up and down inside an engine cylinder which helps convert pressure into energy by pushing against gas or liquid molecules in order to create motion.
Piston Pin & Crank Pin:
A piston pin attaches the piston to its connecting rod while a crank pin connects it all together with the crankshaft which converts linear motion into circular motion allowing for rotation of other parts in the engine such as wheels or pumps.
Piston Ring & Circlip:
A piston ring seals off gas or liquid molecules between two opposing walls which means it helps keep them out of other areas in order to maintain compression ratios when combustion takes place within an engine cylinder while a circlip holds everything together so nothing falls apart during operation.
Poppet Valve:
A poppet valve is a type of valve commonly used in engines. It is designed to open and close quickly and efficiently, using pressure from the engine’s intake manifold or exhaust system. The poppet valve is typically used in combination with other valves, such as the intake and exhaust valves, to regulate airflow into and out of the engine’s cylinders.
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve:
The PCV valve helps reduce emissions by controlling the amount of crankcase vapors released from the engine. It also helps ensure that oil does not become contaminated by these vapors. The PCV valve works by allowing clean air from outside the engine to enter through a tube connected to it, while preventing any gases from escaping back into the atmosphere.
Pulley Part:
Pulleys are used in engines to transfer power from one component to another. The pulley part connects two rotating components together using a belt or chain which allows them to move at different speeds but still deliver power on demand when needed. Pulleys are essential for ensuring that all components are working together efficiently without any unexpected delays or disruptions in power delivery.
Rocker Arm:
The rocker arm is responsible for transferring energy generated by the camshaft into force which pushes against the valves during combustion in order create greater efficiency in terms of fuel economy and performance output. Rocker arms have various shapes and sizes depending on their application but they all serve a similar purpose–to increase efficiency within an internal combustion engine.
Rocker Cover:
Lastly, rocker covers are metal plates located on top of each cylinder head which cover up any exposed valve stems or holes where oil might leak out if there isn’t one fitted securely over them – this ensures optimal performance for both compression & fuel mixture levels within each cylinder resulting in increased overall efficiency & protection against wear & tear damage caused by dust particles getting into those areas!
Starter Motor:
The starter motor engages with your car battery when you turn your ignition key, creating enough torque for your car’s crankshaft so that it can start moving and allow other parts such as pistons, spark plugs etc., to begin working properly for combustion purposes. As its name suggests, it’s one of several parts that make up an internal combustion engine’s starting system – without it, you wouldn’t be able to get your car started!
Starter Pinion:
Starter pinions are small gear-like pieces that attach onto a shaft inside your starter motor with teeth pointed outward like spikes – they act as teeth-grabbers when they link up with another gear called a flywheel ring gear which then rotates clockwise or counterclockwise depending on what type of rotation direction you need for starting purposes – this process creates enough torque so that all other moving parts within your engine can begin functioning properly during startup time!
Starter Ring:
A starter ring is an integral part of the engine that helps turn the engine over when you start it. It consists of a metal ring that fits around the flywheel and connects to the starter motor via solenoid switch. When power is supplied to the starter motor from the battery, the starter ring engages with the flywheel and turns it over to start the engine.
Turbocharger & Supercharger:
Turbochargers and superchargers are both devices used to increase air pressure in an engine’s intake manifold so that more fuel can be burned for increased power output. Turbochargers use exhaust gases produced by an engine to spin a turbine which forces compressed air into the intake manifold while superchargers are powered by an external source such as a belt or electric motor which also forces air into the intake manifold.
Tappet:
Tappets are small metal pieces found in many engines which regulate valve clearance within an engine cylinder head. The tappet has one end that rests against a camshaft lobe while its other end rests against either a valve stem or valve rocker arm depending on its design. As the camshaft lobe rotates it pushes down on the tappet which in turn adjusts valves clearances throughout operation ensuring proper seating of valves when they open and close during combustion events within each cylinder head chamber.
Timing Belt:
A timing belt is a belt made of rubber or synthetic material which runs around two pulleys connected to crankshafts within an engine block allowing them to rotate in sync with one another during operation ensuring pistons fire at their optimum time as well as controlling camshafts rotation providing correct valve duration times during combustion events within each cylinder head chamber.
Timing Tape:
A timing tape is also used in some engines however instead of using a belt this device uses metal strips secured together by rivets for its construction providing similar benefits as above but often offering improved life spans over traditional belts due to their more robust design structure.
Valve Cover:
Valve covers are fitted over cylinder heads on engines controlling oil leakage from around valves by sealing off any gaps between head and cylinder block via gaskets placed between them ensuring no oil escapes during operation preventing excessive wear on seals and gaskets due oil degradation caused by heat build up from combustion events occurring inside each cylinder head chamber whilst also assisting in keeping internal components clean from outside dirt particles entering through gaps created without these covers being present during operation.
Valve Housing
The valve housing is the outer shell of the valve that houses all the other components. It’s made of metal and works as a protective layer to keep dirt and debris out. It also helps to maintain constant pressure around the valve so it can function properly. Valve housings come in many different shapes and sizes depending on what type of valve you have installed in your vehicle. Make sure to check with your mechanic or research online to determine which type is right for your engine before replacing it.
Valve Spring
The valve spring is the part that actually opens and closes the valve when needed. It’s a flat metal coil that sits between two pieces of metal, known as retainer clips, which hold it in place. The force generated by the spring allows it to open and close quickly, regulating air flow into and out of the engine chamber. Without a functioning valve spring, your engine won’t be able to perform efficiently or safely.
Valve Stem Seal
The valve stem seal is an important component because it prevents oil from entering into the combustion chamber when the engine is running at high RPMs. It also ensures that there isn’t any leakage when you shut off your engine after a long drive or race day event. If this seal fails then oil will leak into other parts like spark plugs or even onto the ground beneath your vehicle – causing costly repairs if not caught early enough! Make sure to check this seal frequently during routine maintenance sessions!
Water Pump Pulley
The water pump pulley is responsible for spinning the water pump impeller so coolant can circulate throughout your entire cooling system while keeping temperatures low during extended periods of use or heavy workloads such as racing events where temperatures can soar above normal levels without proper care taken ahead of time! This pulley must remain tightly mounted onto its shaft at all times otherwise there may be vibration issues that can damage other parts inside your engine bay – make sure all bolts are securely tightened before use!
Conclusion:
Keeping track of all these different components and parts can seem daunting at first but understanding how they work together will help ensure your car runs smoothly for many miles ahead! It’s important to remember that regular maintenance for each component is essential if you want them all working together properly without any hiccups along the way! Knowing what each part does will help you identify any potential problems before they become more serious issues down the line – so get informed today!