What is a Rotameter:
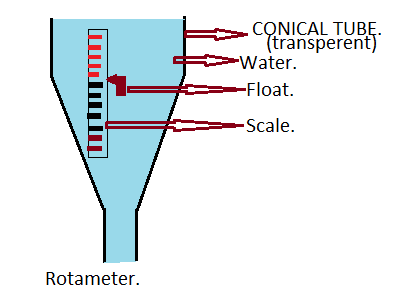
Rotameter: Rotameter is a fluid flow rate measuring device which is also called a variable area meter. This device has a long vertical tube which is transparent to view the measurements on a scale, which is according to the flow of fluid through it. to recording this measurement there is an electrical transmitter.
Construction of a Rotameter:
Transparent tube:
This tube is in a conical shape which has a measurement scale and floats inside it, this transparent tube helps to see the measurements directly.
Float:
Float is small equipment with accurate dimensions placed inside the tube which helps to indicate the flow rate in the tube. this can be made with glass, metals or plastic.
Scale:
Scale shows the measurements of flow by indicating with float.
Transmitters:
This device helps to record the measurements accurately than we see on the scale directly. they work with an electricity supply.
Working of a rotameter:
The fluid in rotameter used to flow from downwards to up and in the middle of the device there is a scale which used to given an output flow rate, when the fluid flow
takes place there is an increase or decrease in flow by this flow the float used to move up and down according to the flow init. due to the presence of float in the tube, there is a head loss occurs, this loss is equal to the weight of the float.
Advantages of a rotameter:
- We can find the rate of flow by direct visual.
- There is a low-pressure loss in it.
- Cost of this equipment is less.
- Easy in construction.
- We can work on it directly, without any sample flows.
Disadvantages of a rotameter:
- Accurate measurements are not possible init.
- This is not used where there is fast changes occur in measurements.
Applications of a rotameter:
- Highly used in industries.
- It used where there is a quality supply of air is needed.
- This is used at low pressure is required eg: gases.