working of Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT):
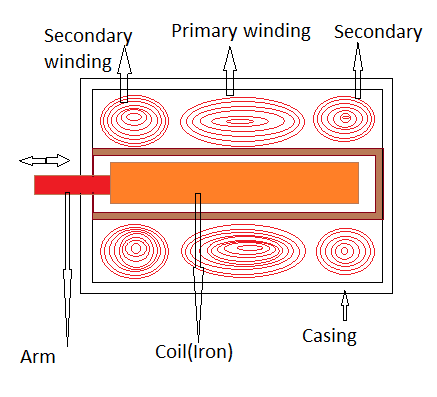
- A Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) consists of one primary winding and two secondary windings with the equal number of turns wound on a cylindrical former. The two secondary windings are connected in series opposition and are placed identically on either side of the primary winding to which an AC excitation voltage is connected. A movable soft iron core is placed within the cylindrical former. When the displacement to be measured is applied to the arm of the core, the LVDT converts this displacement into an electrical signal. The operation of the LVDT principle depends on mutual inductance. When the primary winding is supplied with AC supply voltage, it generates an alternating magnetic field. Due to this magnetic field, an alternating voltage will be induced in the two secondary Windings.
Construction of LVDT
Advantages of LVDT:
- LVDT has very good linearity.
- It can measure displacements of very high range usually from 1.25mm to 250mm.
- It has high sensitivity.
- It has low hysteresis.
- It consumes less power.