Difference between Synchronous AC Motor & Permanent Magnet Motor:
The Main Difference between Synchronous AC Motor & Permanent Magnet Motor
Synchronous AC Motor:
- The synchronous AC motor consists of a stator and a rotor. The stator is cylindrical and has several coils around its surface. The rotor sits inside the stator and has several poles, one for each coil on the stator.
- As synchronous motors contain an internal voltage regulator, the starting torque is nearly constant throughout the whole process of acceleration as well as the synchronous speed.
- AC synchronous motor has been widely used in many fields because it does not need to use the excitation field synchronous generator, synchronous motors can produce a large starting torque.
- They have no permanent magnets and need two main components to start rotating, a short-circuited rotor winding and an applied voltage.
- Synchronous motors have high efficiency, good controllability. It is suitable for all kinds of load, the speed regulation range is very wide.
- AC synchronous motor is normally used as a synchronous generator or synchronous alternator. The synchronous motor has an output voltage, the speed of the synchronous machine determines the speed at which this output voltage is generated and hence determines the frequency of mains electricity (50 Hz or 60 Hz).
- Synchronous motor work as a turbine and the direction of power generation can be changed by switching the polarity of each phase.
- Synchronous motor is usually used in very large applications such as electricity transmission (for example, as part of high voltage direct current (HVDC) systems), railway traction.
Permanent Magnet Motor:
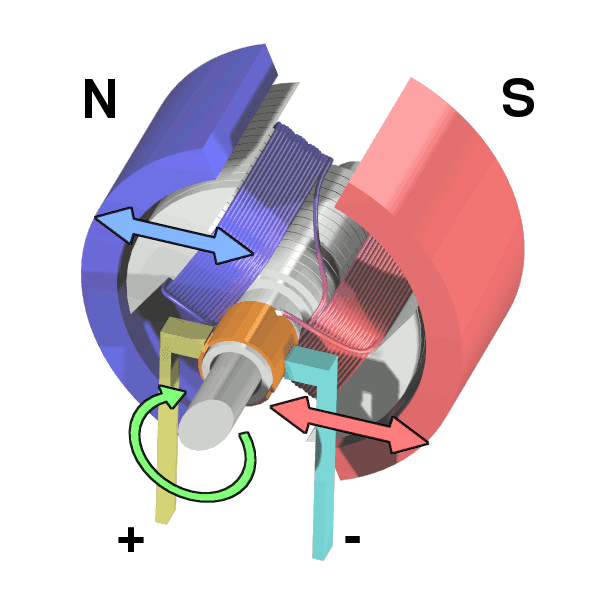
- A permanent-magnet motor (PMM) is a type of electric motor that uses permanent magnets to create the rotating magnetic fields required to turn the rotor.
- Permanent-magnet motors offer very high starting torque and smooth running but require external electrical power (AC mains) to be turned by the rotor.
- Permanent-magnet motors are used in many simple devices such as ceiling fans, the hub of a wheel, or a mechanism for opening and closing valves.
- Permanent magnet machines can be made to run on AC power (a modified standard type) and they also offer high efficiency and drivability at low noise levels.
- Permanent magnets can be used to make motors with fewer moving parts.
- These are expensive than Synchronous motors.
- The rotor speed is less than the Synchronous motors.
- It has large power per unit weight.
- Permanent-magnet traction drives (PMLTD) are now being used in some locomotives, streetcars, and electric vehicles. AC
- Permanent magnets will not lose their magnetism unless they are heated to the point where they become demagnetized.
Permanent Magnet Motor (Image Source: wikipedia.org)
Synchronous AC Motor Vs Permanent Magnet Motor
| Synchronous AC motors | Permanent magnet motors |
|---|---|
| The synchronous AC motor consists of a stator and a rotor. The stator is cylindrical and has several coils around its surface. The rotor sits inside the stator and has several poles, one for each coil on the stator. | Permanent-magnet motors are used in many simple devices such as ceiling fans, the hub of a wheel, or a mechanism for opening and closing valves. |
| They have no permanent magnets and need two main components to start rotating, a short-circuited rotor winding and an applied voltage. As synchronous motors contain an internal voltage regulator, the starting torque is nearly constant throughout the whole process of acceleration as well as the synchronous speed. | Permanent-magnet motors offer very high starting torque and smooth running but require external electrical power (AC mains) to be turned by the rotor. |
| AC synchronous motor has been widely used in many fields because it does not need to use the excitation field synchronous generator, synchronous motors can produce a large starting torque and they have a lot of advantages such as high efficiency, good controllability. | Roland Mendel |
| It is suitable for all kinds of load, the speed regulation range is very wide. | Permanent magnet machines can be made to run on AC power (a modified standard type) and they also offer high efficiency and drivability at low noise levels. |
| AC synchronous motor is normally used as a synchronous generator or synchronous alternator. | Yoshi Tannamuri |
| The synchronous motor has an output voltage, the speed of the synchronous machine determines the speed at which this output voltage is generated and hence determines the frequency of mains electricity (50 Hz or 60 Hz). | Permanent-magnet traction drives (PMLTD) are now being used in some locomotives, streetcars, and electric vehicles. Permanent magnets can be used to make motors with no moving parts. |
| AC synchronous motor work as a turbine and the direction of power generation can be changed by switching the polarity of each phase. | A permanent-magnet motor (PMM) is a type of electric motor that uses permanent magnets to create the rotating magnetic fields required to turn the rotor. Permanent magnet motors are very. |
| Synchronous AC synchronous motor is usually used in very large applications such as electricity transmission (for example, as part of high voltage direct current (HVDC) systems), railway traction | Permanent magnets will not lose their magnetism unless they are heated to the point where they become demagnetized. |