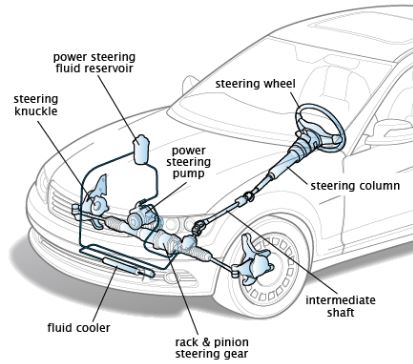
Difference between Single Phase and Three Phase Generators?
Single Phase Generator:
- Single-phase generators are the most common type of generator used in residential and commercial applications. They use a single rotating armature to produce electrical power.
- Single-phase generators are also called single-winding generators or unipolar generators.
- A single-phase generator is the type of generator that only has one electrical winding and thus produces a single-phase current.
- The single-phase is more prone to line losses and voltage drops because it has no balancing mechanism.
- Single-phase generators do not require any external source of power.
- Single-phase generators tend to be less expensive than their three-phase counterparts due to lower manufacturing costs.
Three Phase Generator:
- Three-phase generators have three rotating armature coils, which rotate at different speeds to produce electricity that is compatible with three-phase power systems.
- The three-phase generators are more common in power generation because they have three separate electrical windings which can produce three-phase currents.
- Three-phase generators can handle high loads at low or medium speed without producing excess vibrations or noise.
- A three-phase generator’s distribution of power among phases makes it possible to operate at different speeds without losing any efficiency.
- Three-phase generators are better because they use an extra winding that creates a balance between the phases, which means they have less line loss and lower voltage drops.
- Three-phase generators can produce more power than a single-phase generator of the same size.
- Three-phase generators are typically used for power generation whereas single-phase generators are commonly used in industrial applications like manufacturing and mining where the process does not require any spinning or rotating machinery.
- Three-phase generators are more efficient and cost-effective than single-phase generators.
- Three -phase generators are used in large projects where the risk of overloading is high.
- Three-phase generators offer superior performance and reliability over single-phase generators.
- Three-phase generator has an improved dynamic range, which means it can be run at a higher voltage than a two- or four-wire system. This feature makes it more suitable for use in distribution systems with multiple transformers to handle high loads.
- Three-phase generators have increased insulation levels, which allows them to withstand transient overloads from faults and help prevent equipment damage from excessive harmonics.
- Three-phase generators reduce energy losses due to lower magnetic leakage currents and no eddy currents generated by the transformer windings when compared to single-phase generators.
Single Phase Generator (Source: wikimedia.org)