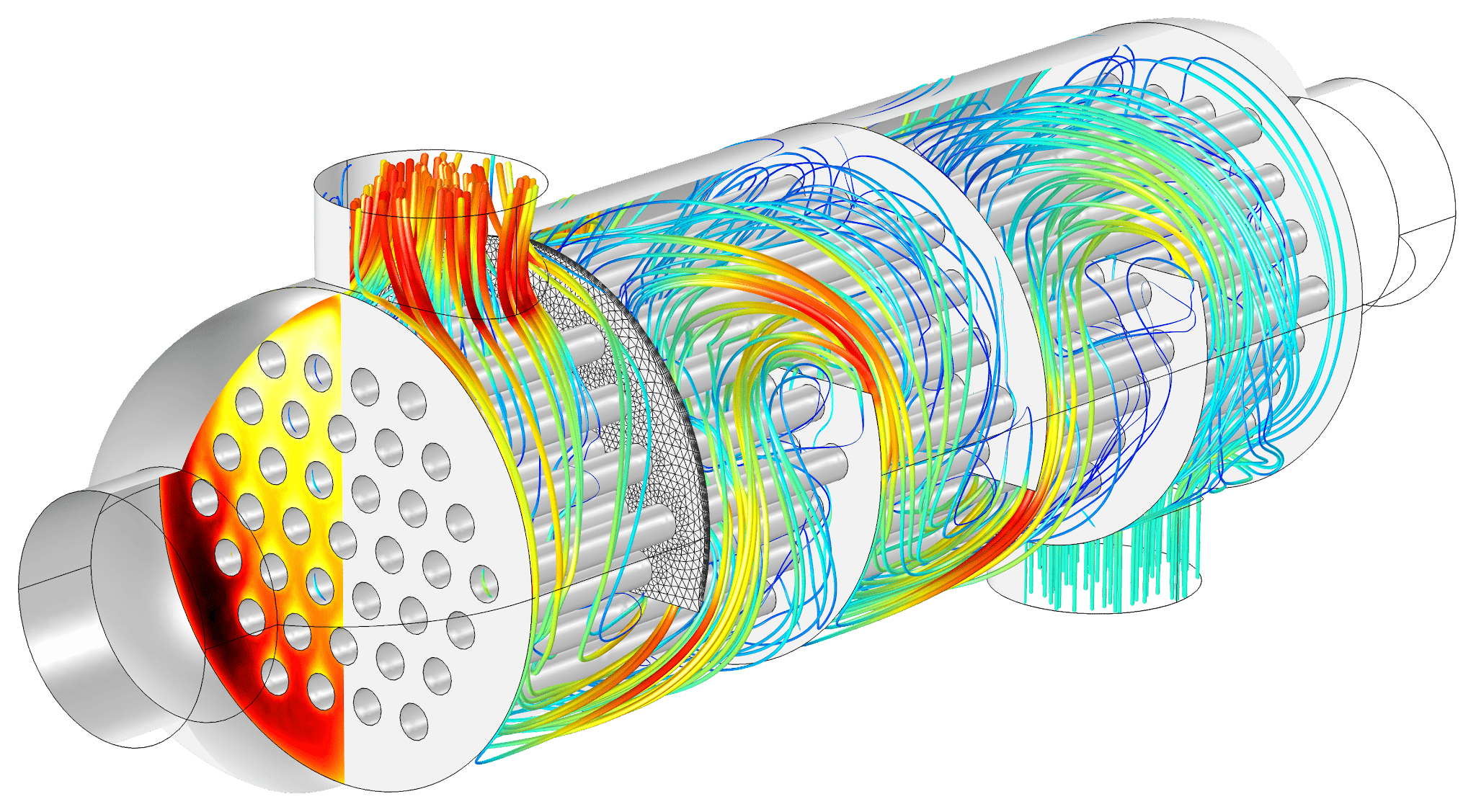
Difference between the Heat Exchanger and Condenser?
Heat Exchanger:
- The heat exchanger is a device that is used to transfer heat from one place to another.
- The heat exchanger is the part of a refrigerator that separates hot and cold air, while the condenser cools it down.
- The heat exchanger is a device that uses the difference in temperature between two different fluids to transfer heat energy from one fluid to another.
- The heat exchanger separates the hot and cold liquids in an evaporator. The condenser is a device that cools liquid from one or more heat exchangers.
- Heat exchangers do not require the use of refrigerants, which means they are environmentally friendly.
- A heat exchanger can be used in any location where the temperature difference between two fluids is about 100 degrees Fahrenheit or more.
- Heat exchangers use the same amount of energy as a condenser, but they need more time for installation because they are larger in size and require more components.
- Heat exchangers are typically used in industrial settings where large amounts of energy are required for heating or cooling systems.
- Heat exchangers can handle higher pressures.
- The advantages of a heat exchanger over a condenser are that the former is more cost-effective and is less prone to damage. The main reason for this is that it does not have moving parts, unlike a condenser.
Condenser:
- Condenser transfers heat from a cool area to a hot area.
- Condensers are usually found in HVAC applications such as air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
- A condenser is an apparatus that cools a fluid by evaporating and condensing it.
- A condenser is a device that changes the phase of fluid from liquid to gas.
- Condensers are generally more efficient than heat exchangers because they transfer all the heat in one direction (as opposed to two).
- Condensers are often smaller and more compact than conventional systems.
- Condensers require less maintenance than a conventional system.
- Condensers require less energy to operate than Heat exchangers.
- Condensers are more durable and reliable because the design is more precise.
- Less installation time is required with condensers due to their smaller size and simpler configuration.
There are two types of heat exchangers:
Crossflow and Counterflow.
Cross-flow devices have air going through the tubes whereas, counter-flow devices have liquid flowing through the tubes.