Difference Between Belt Drive and Gear Drive?
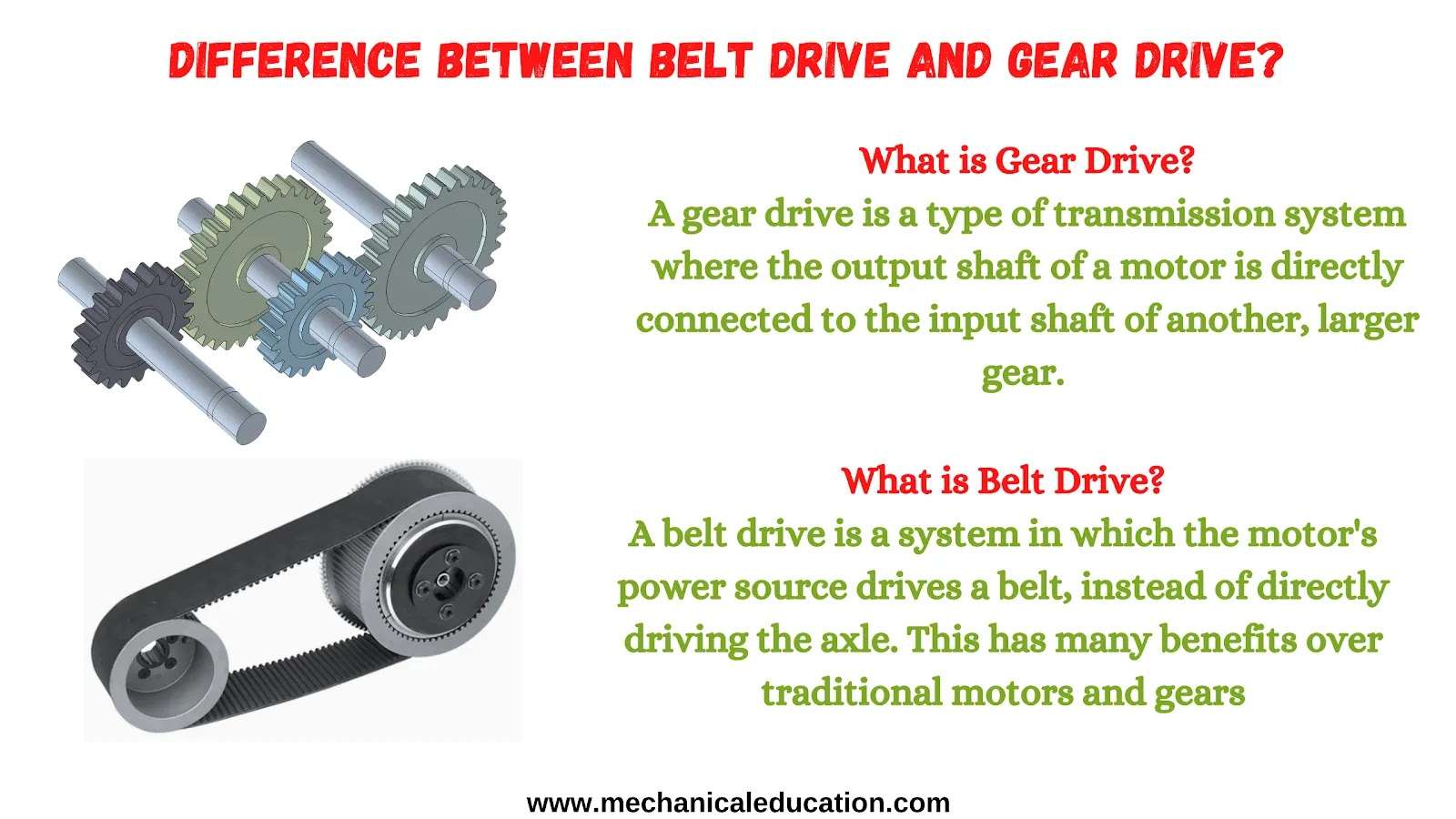
What is Gear Drive?
A gear drive is a type of transmission system where the output shaft of a motor is directly connected to the input shaft of another, larger gear.
In most cases, this is achieved by using gears on both ends. It allows for smoother and more efficient power transfer between two rotating shafts than would be possible with a belt or chain.
What is Belt Drive?
A belt drive is a system in which the motor’s power source drives a belt, instead of directly driving the axle. This has many benefits over traditional motors and gears
Gear drive:
- Gear drive is more efficient.
- Gear drive produces less wear and tear on the machine.
- Gear drives also do not require a great deal of care and management, as the gears themselves maintain their oil film.
- Gear drive is more complex to build.
- Gears are more precise.
- Gear Drives are known to be quieter and smoother.
- Gear Drives are Expensive.
Belt Drive:
- Belt drives are less efficient.
- Belt drive tends to have more wear and tear compared to gear drive.
- The belt drive does not require regular maintenance.
- Reduction of heat – since the belts do not require lubrication, they will not generate any friction or heat when running for long periods of time.
- A belt drive is less complex to build than a gear drive.
- Belt Drive has good longevity, but gears are more precise.
- A belt drive is not as smooth as a gear drive.
- Belt drives are less expensive.
Different Between Gear drive and Belt Drive?
Both have versatility in terms of moving at different speeds, but belt drives work better in applications where speed up or down is undesirable.
Gears can be smaller than belts since they have a larger area for the teeth which allows them to take up less room in tight spaces.
Belt cogs do not suffer fatigue failure like teeth of driving gears do.
Belt drive transmissions tend to wear out much faster when used with high torque loads because the belt slips when it flexes too much. Gearing can flex due to how tight it is so there isn’t as big an issue with wearing out when you have heavy loads.
One strong advantage of a belt drive is its simplicity since no gears are involved in delivering power to its final destination – all it needs is rubber tires and some torque which isn’t too high relative
Belt Drive postulates that the belt is more efficient than gears because it avoids loss of power since there is no contact between metal-to-metal. The first few teeth of the drive gear transmit some forces through to the attached pulley and sheave, which contains all other non-driving gears, so it rotates at approximately full speed. All other teeth on the drive cog are either above or below its adjacent driven cog so they ride without contacting each other. As a result, belt cogs do not suffer fatigue failure like teeth of driving gears do.
Gear Drive postulates that belts can slip (unlike gears) and that this slipping provides energy loss; however, this isn’t an issue.