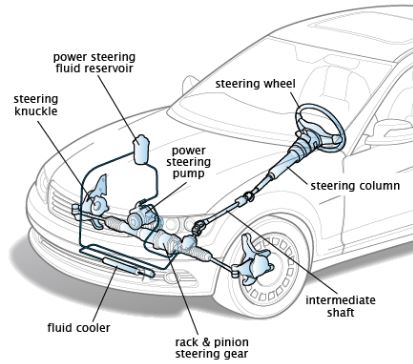
A kinematic chain is a series of interconnected kinematic links that are used to transmit motion or force within a mechanical system. A kinematic chain consists of a series of interconnected links that form a closed loop, with each link connected to at least one other link through a joint. The links in a kinematic chain can be either rigid or flexible, and the joints can be either lower pairs or higher pairs, depending on the type of motion that they allow.
Kinematic chains are used to transmit motion or force between different parts of a mechanical system and can be combined to form more complex mechanisms. They are an important element in the design and analysis of mechanical systems, as they play a crucial role in transmitting motion and force within the system.
Some examples of kinematic chains include:
- Linkages: These are kinematic chains that consist of a series of interconnected rigid links and joints, and they are used to transmit motion or force between different parts of a mechanical system.
- Belts and chains: These are kinematic chains that consist of a series of interconnected flexible links, and they are used to transmit motion or force between different parts of a mechanical system.
- Human limbs: The arms and legs of the human body can be considered as kinematic chains, as they consist of a series of interconnected links and joints that are used to transmit motion or force.
Kinematic chains are an important element in the design and analysis of mechanical systems, as they play a crucial role in transmitting motion and force within the system.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a kinematic chain in mechanical engineering?
A kinematic chain is a series of interconnected links or elements designed to transmit motion and force, forming a closed or open structure. It is a fundamental concept in mechanical engineering used to analyze and understand the motion of interconnected parts.
2. How is a kinematic chain different from a mechanism?
While a kinematic chain represents a set of interconnected links without specifying the input or output, a mechanism is a kinematic chain with a designated input and output, demonstrating a specific purpose or function.
3. What are the primary elements of a kinematic chain?
The primary elements of a kinematic chain include links, joints, and a mechanism. Links represent rigid bodies, joints are connections allowing relative motion, and a mechanism is the combination of links and joints forming a functional system.
4. Can a kinematic chain be both open and closed?
Yes, a kinematic chain can be either open or closed. An open kinematic chain has one or more free ends, while a closed kinematic chain forms a complete loop with no free ends. Machines often use both types in various configurations.
5. How is the degree of freedom determined in a kinematic chain?
The degree of freedom in a kinematic chain is determined by counting the number of independent motions or variables required to specify its configuration. It represents the number of inputs needed to define the position of all links in the chain.
6. Are there different types of kinematic chains?
Yes, kinematic chains can be classified based on their structure. Some common types include serial chains (linear sequence of links), parallel chains (multiple paths for motion), and complex chains that combine both serial and parallel elements.
7. Can a kinematic chain exhibit constrained motion?
Yes, a kinematic chain can exhibit constrained motion when certain joints or connections limit the range of motion of specific links. Constraints are crucial in analyzing the behavior and stability of the chain.
8. How is a kinematic chain analyzed in engineering applications?
Engineers use various methods, including graphical methods, mathematical equations, and computer simulations, to analyze kinematic chains. These techniques help determine motion characteristics, velocities, accelerations, and other performance aspects.
9. What is the significance of kinematic analysis in machine design?
Kinematic analysis in machine design is crucial for predicting and understanding the motion of mechanical components. It aids in optimizing designs, ensuring proper functionality, and identifying potential issues related to speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
10. Can a kinematic chain be found in everyday objects?
Yes, kinematic chains are found in various everyday objects and machines. Examples include door hinges, bicycle linkages, robotic arms, and the human body’s skeletal structure. Understanding kinematic chains is essential for designing and improving mechanical systems in daily life.