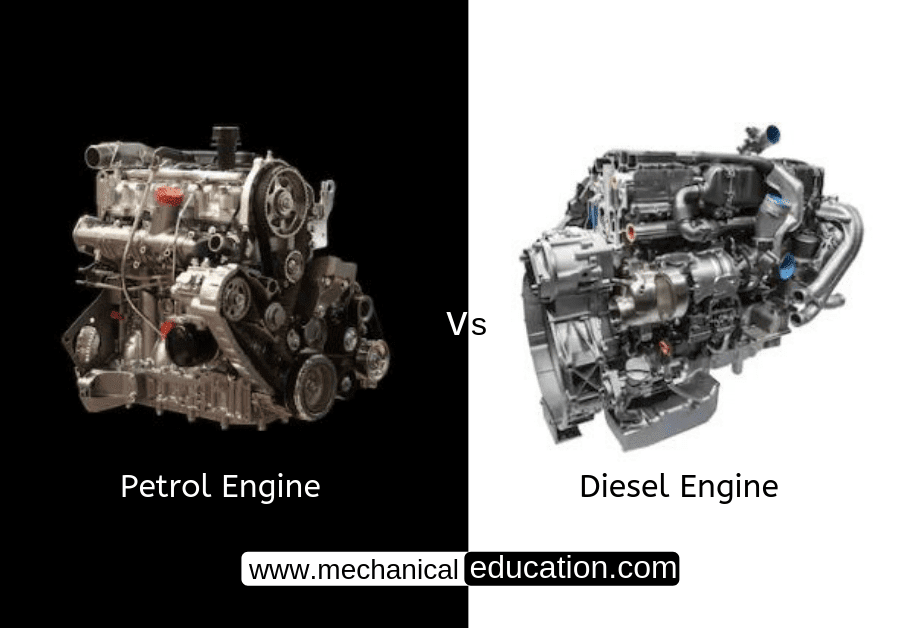
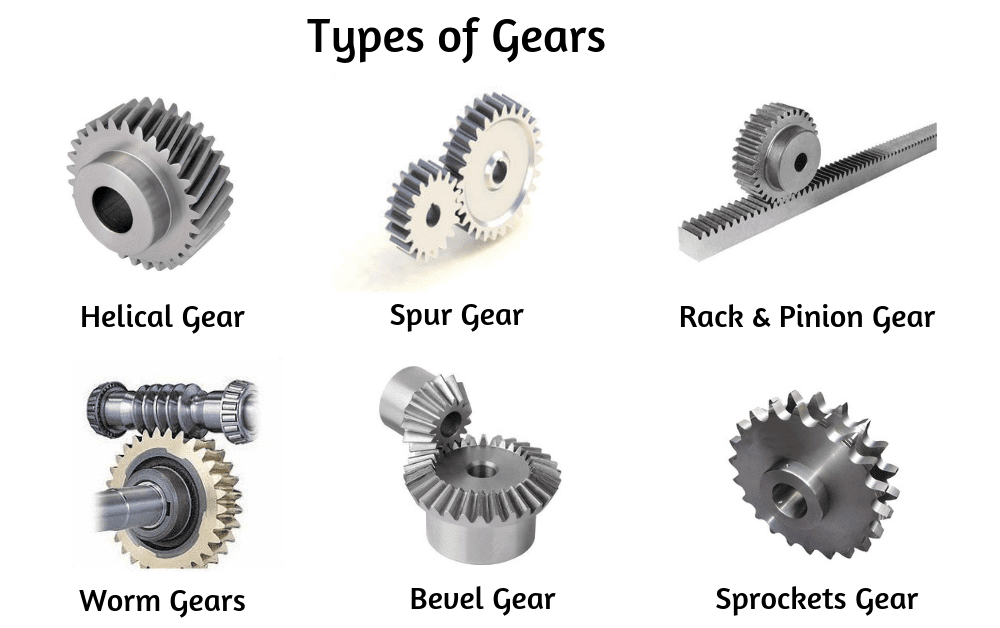
Introduction: Gears are one of the most important components in any mechanical system. They are used to transfer power between two shafts in a fixed ratio, and also to change the speed or direction of the rotating shaft. In this article, we will discuss some of the most common types of gear mechanisms that are used in everyday machines.
Gear Coupling
A gear coupling is a device used to connect two rotating shafts together, allowing them to rotate at different speeds while maintaining a constant drive ratio. It consists of two metal plates with interlocking teeth on each plate that mesh together when connected, preventing any relative motion between them. This makes it an ideal choice for applications that require accurate control over the speed and torque output from one shaft to another.
Gear Pump
A gear pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses intermeshing gears to move fluid from an inlet port to an outlet port. They are widely used in industrial applications where precise amounts of liquids need to be moved quickly and efficiently. The advantage of using a gear pump is that they are able to operate at very high pressures, making them ideal for applications such as hydraulic systems and fuel injection systems.
Gear Ring
A gear ring is a circular piece of metal with teeth cut into its surface, which can be used to transmit rotary motion between two rotating shafts. It works by engaging the teeth on each side of the gear ring into corresponding grooves on each shaft, allowing them to rotate at different speeds while still achieving a constant drive ratio. This type of mechanism is often found in automatic transmissions and differential gearsets.
Gear Stick (gear-stick, gear lever, selection lever, shift stick, gear shifter)
The term “gear stick” refers to any lever or knob used for changing gears in manual transmission vehicles or machinery. It can be located on the floor near the driver’s seat or mounted on the dashboard or console near the shift selector knob. Its purpose is to allow you to select which gear you want your vehicle or machine to run in by pushing or pulling it up or down accordingly—for example from park (P) into drive (D).
Gearbox
A gearbox is a mechanical device that transmits power from an input source (usually an engine) through a series of gears and cogs to an output source (usually a wheel). This allows for precise control over how much power is transmitted at any given time, as well as providing adjustable gearing ratios so that you can achieve different drive characteristics depending on what type of driving you’re doing—such as city driving versus highway cruising. Gearboxes are typically used in automotive transmissions and other heavy machinery like construction equipment and agricultural equipment.
Idler Gear
An idler gear is a small wheel with teeth cut into its circumference which allows it to engage with other larger wheels within a mechanical system—such as those found in transmissions or differential gearsets—without actually transferring any power itself. Idler gears provide additional support for larger components within these systems by taking up space between them so they don’t come into contact with each other when rotating at high speeds; this helps prevent wear and tear on these components over time due to friction caused by their movement against one another.
Conclusion:
Gears play an integral role in many machines across multiple industries—from cars and trucks all the way down to tiny toys powered by clockwork mechanisms! Understanding how these various types work can help you gain insight into how machines operate more effectively and efficiently, giving you better control over their performance overall! Whether it’s understanding how your car works under the hood or being able to identify various types of gears within complex machinery you encounter throughout life; having knowledge about these essential components will give you greater insight into how things work!