D.C Arc Welding Advantages and Disadvantages
What is D.C Arc Welding?
DC arc welding is a process of joining metal by using an electric current. The voltage is generated in the welder and then delivered to the workpiece. This allows you to weld with different metals without the need for high-frequency, pulsed currents that require high voltages and produce more heat than what is needed.
A wire electrode, usually made from tungsten or a tungsten alloy, creates an arc between two electrodes which delivers electricity into the material being welded.
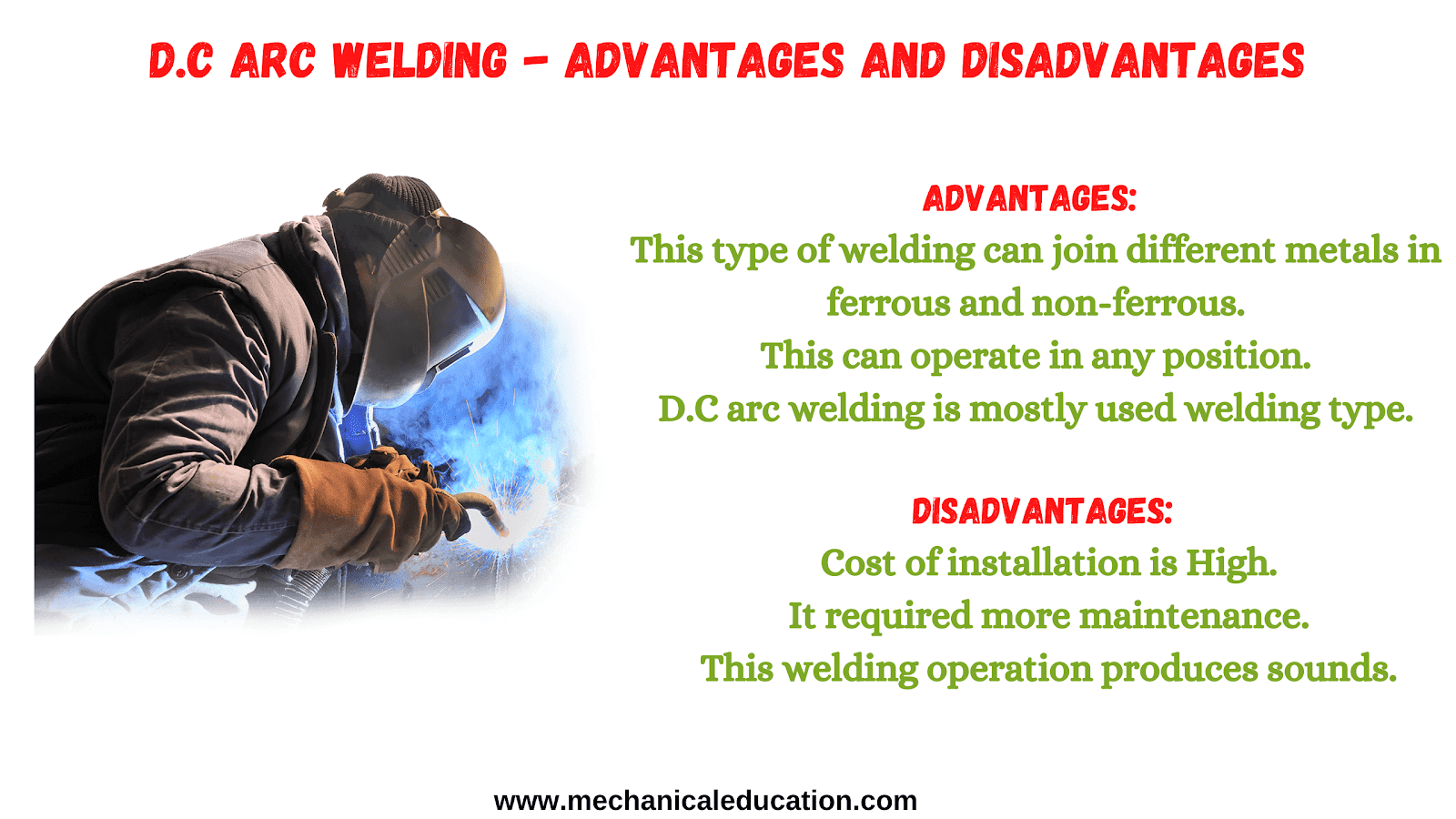
Advantages of D.C Arc Welding:
- This type of welding can join different metals in ferrous and non-ferrous.
- This can operate in any position.
- D.C arc welding is mostly used welding type.
- The arc is more stable, which makes it easier to control.
- It’s less likely to cause spatter, which can damage the weld and the surrounding area.
- It creates a less intense heat, which can be better for thin metals or delicate materials.
- It produces less smoke and fumes than other types of welding.
- It is very smooth and does not create a lot of spatter.
- It is also very forgiving because it is easy to stop the arc and start again without creating a lot of damage.
- The welding process can be precisely controlled in both width and depth of penetration, results look cleaner when done by an experienced operator.
Disadvantages of D.C Arc Welding:
- Cost of installation is more.
- It required more maintenance.
- This welding operation produces sounds.
- Deformation of the workpiece may occur.
- It doesn’t work as well with thicker metals.
- The arc is more likely to start breaking up if there’s too much current variation.
- It is not as strong as AC welding, and it can be more difficult to weld certain metals with this process.
- It uses a high-voltage system, produces far more dangerous arcs than AC welding, has a slower speed of application because the metal must be melted before it is drawn into the arc.
- It is less efficient at very low voltages or currents.