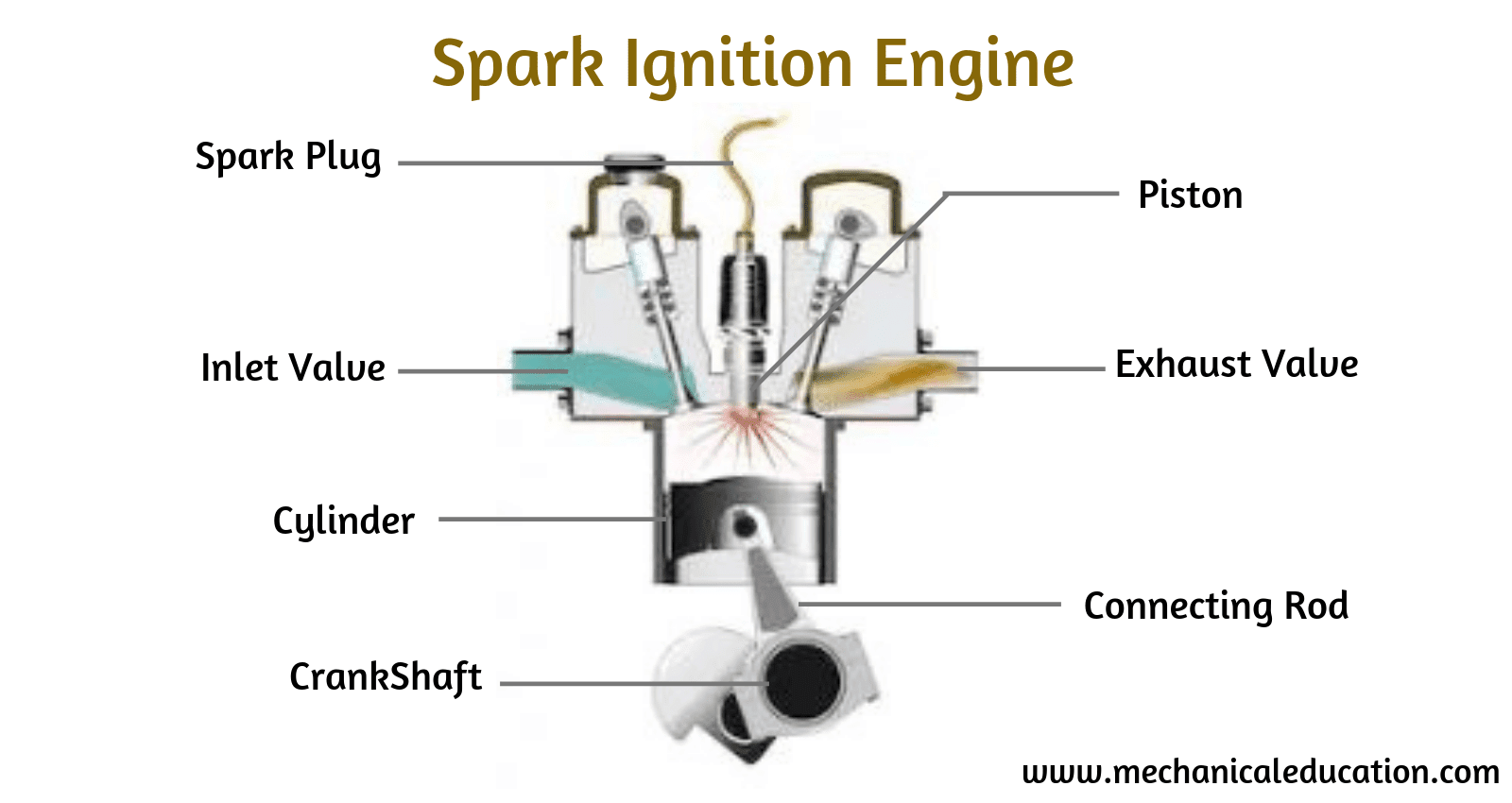
A car engine can experience knocking, also known as engine knock or detonation, when the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber explodes or ignites in an uncontrolled manner. This can occur due to various factors, including:
Low octane fuel:
If you use a gasoline with an octane rating lower than what is recommended for your vehicle, it can lead to knocking. Octane rating indicates the fuel’s resistance to detonation. Lower octane fuel ignites at lower pressures, which can cause knocking.
Carbon deposits:
Over time, carbon deposits can accumulate on the inside of the combustion chamber, including the piston crown and cylinder walls. These deposits can become hot spots and cause the air-fuel mixture to ignite prematurely, leading to knocking.
Incorrect ignition timing:
The spark plugs in an engine ignite the air-fuel mixture at a precise time. If the ignition timing is too advanced, meaning the spark plug fires too early, it can cause knocking.
Overheating:
When an engine runs too hot, it can cause the fuel to ignite before the spark plug fires. High engine temperatures can be caused by factors such as a malfunctioning cooling system, low coolant levels, or a faulty thermostat.
Excessive engine load:
If you put too much load on the engine, such as accelerating hard or towing a heavy load, it can increase the cylinder pressure and temperature, leading to knocking.
Mechanical issues:
Engine components, such as the piston rings, valves, or connecting rod bearings, can wear out or become damaged over time. These issues can alter the combustion process and contribute to knocking.
Fuel quality or contamination:
Poor quality or contaminated fuel can cause knocking. It may contain impurities or additives that affect the combustion process and lead to detonation.
It’s important to address engine knocking promptly, as prolonged knocking can cause damage to the engine. If you experience persistent knocking, it’s recommended to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic to diagnose and resolve the underlying cause.
Frequently asked questions
1.What is engine knock, and how is it characterized?
Engine knock, also known as detonation, is an undesirable condition where fuel-air mixture ignites spontaneously in the combustion chamber before the spark plug fires, creating a knocking or pinging sound.
2.What causes engine knock?
Engine knock is often caused by using low-octane fuel, incorrect ignition timing, carbon buildup in the combustion chamber, overheating, or a malfunctioning knock sensor.
3.Can using the wrong type of fuel lead to engine knock?
Yes, using a lower octane fuel than recommended for your vehicle can result in engine knock. Higher octane fuels resist premature combustion and help prevent knocking.
4.How does incorrect ignition timing contribute to engine knock?
If the ignition timing is too advanced, the air-fuel mixture may ignite too early, leading to engine knock. This is why proper timing adjustment is crucial for engine performance.
5.Can a dirty or clogged fuel injector cause engine knock?
Yes, dirty or clogged fuel injectors can disrupt the fuel spray pattern, affecting combustion and potentially causing engine knock. Regular maintenance, including fuel system cleaning, can help prevent this.
6.Is engine knock harmful to the engine?
Yes, persistent engine knock can lead to serious damage over time. It can cause piston and cylinder damage, leading to expensive repairs if not addressed promptly.
7.How does the knock sensor contribute to preventing engine knock?
The knock sensor detects vibrations or noises associated with engine knock and sends signals to the engine control unit (ECU), which then adjusts the ignition timing to mitigate the issue.
8.Can overheating contribute to engine knock?
Yes, overheating can increase the risk of engine knock. High temperatures can cause pre-ignition of the fuel-air mixture and contribute to detonation. Regular cooling system maintenance is essential.
9.Can changes in altitude or weather affect engine knock?
Yes, changes in altitude and weather conditions can impact air density, affecting the air-fuel mixture. Engines may need adjustments to prevent or minimize knock under different environmental conditions.
10.How can engine knock be prevented or remedied?
To prevent engine knock, use the recommended octane fuel, maintain proper ignition timing, keep the engine well-tuned, use quality fuel injectors, and ensure the cooling system is in good condition. If knock is detected, addressing the root cause promptly is crucial to prevent further damage.