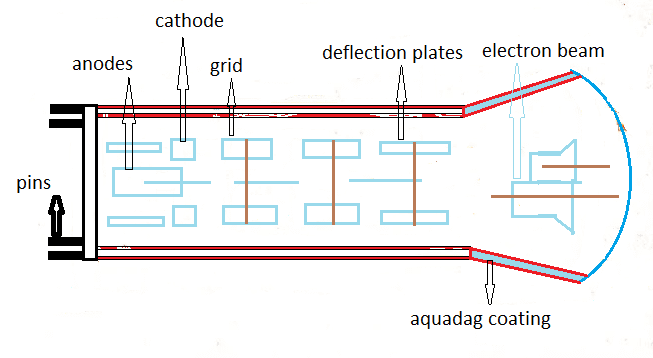
There are several 3D modeling software used for mechanical engineering, including SolidWorks, Creo, and CATIA. Each software has unique features and capabilities that make it suitable for specific applications. Here are some key differences between these software:
| Features | SolidWorks | Creo | CATIA |
| Design capabilities | SolidWorks is specifically designed for mechanical design and engineering, including the creation of parts, assemblies, and drawings | Creo has advanced part design capabilities, including parametric modeling, simulation, and analysis | CATIA is a comprehensive software suite that can be used for a wide range of applications, including mechanical design, aerospace, automotive, and industrial design |
| Modeling approach | SolidWorks uses a feature-based modeling approach that allows for the creation of complex, parametric models | Creo uses a parametric modeling approach that allows for the creation of intelligent, associative models | CATIA uses a hybrid modeling approach that allows for the creation of both feature-based and parametric models |
| Assembly design | SolidWorks is specifically designed for assembly design, including advanced features such as interference detection and motion analysis | Creo has advanced assembly design capabilities, including interference detection, clearance analysis, and motion simulation | CATIA has comprehensive assembly design capabilities, including advanced kinematic analysis and mechanism design |
| Simulation and analysis | SolidWorks has advanced simulation and analysis tools, including finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and motion analysis | Creo has advanced simulation and analysis capabilities, including FEA, CFD, and kinematic analysis | CATIA has a wide range of simulation and analysis capabilities, including FEA, CFD, and kinematic analysis, as well as specialized tools for automotive and aerospace applications |
| Industry | SolidWorks is primarily used in the manufacturing and mechanical engineering industries | Creo is used in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and consumer products | CATIA is used in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, industrial design, and architecture |
In summary, SolidWorks is specifically designed for mechanical design and engineering, with advanced capabilities for part and assembly design, simulation, and analysis. Creo also has advanced part design and assembly design capabilities, with a focus on parametric modeling and simulation. CATIA is a comprehensive software suite that can be used for a wide range of applications, including mechanical design, aerospace, automotive, and industrial design, with a hybrid modeling approach and a wide range of simulation and analysis capabilities.
It is important to note that the choice between these software ultimately depends on the specific needs and preferences of the user, as well as the industry and application. Some firms may use multiple software in conjunction with each other, depending on the project requirements.
Frequently asked questions
1.What are the key differences between popular 3D modeling software used in mechanical engineering, such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and CATIA?
While all three are powerful tools, they differ in terms of user interface, parametric modeling capabilities, and industry focus. AutoCAD is known for its versatility, SolidWorks for parametric design, and CATIA for its extensive capabilities in aerospace and automotive industries.
2.Which software is better for beginners in mechanical engineering?
AutoCAD is often considered more beginner-friendly due to its intuitive interface and widespread use. SolidWorks, while powerful, may have a steeper learning curve for beginners.
3.Can designs created in one software be easily transferred to another?
Transferring designs between software can be challenging due to differences in file formats and parametric modeling methods. It often requires file conversion and may result in some loss of information.
4.What makes SolidWorks stand out in mechanical engineering applications?
SolidWorks is renowned for its parametric modeling capabilities, making it highly efficient for creating complex 3D models and assemblies. Its user-friendly interface and extensive community support contribute to its popularity.
5.In which industries is CATIA commonly used for mechanical engineering?
CATIA is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and other industries with complex design and engineering requirements. Its robust surface modeling and assembly capabilities make it suitable for advanced projects.
6.Can AutoCAD be used for 3D modeling in mechanical engineering?
Yes, AutoCAD has 3D modeling capabilities, making it suitable for mechanical engineering. However, it is often more recognized for 2D drafting and general-purpose design.
7.How does the cost of these software solutions compare?
AutoCAD is generally more affordable compared to SolidWorks and CATIA. SolidWorks is moderately priced, while CATIA, with its advanced features, tends to be on the higher end in terms of cost.
8.Are there significant differences in the collaboration features of these software solutions?
Collaboration features vary, with all three supporting collaboration to some extent. SolidWorks offers tools like PDM for data management, while CATIA emphasizes collaboration in large-scale projects.
9.Can these software solutions be used for simulation and analysis in mechanical engineering?
Yes, all three software solutions offer simulation and analysis tools. SolidWorks Simulation and CATIA V5 Analysis, for example, provide comprehensive capabilities for stress analysis, thermal analysis, and more.
10.Which software is more suitable for large-scale projects in mechanical engineering?
CATIA is often preferred for large-scale projects, especially in aerospace and automotive industries, due to its robust parametric modeling, surface modeling, and collaborative features tailored for complex projects.